Brooke Jude Discusses Her Collaboration with Microbiologist Anne Madden to Save Amphibians
Associate Professor of Biology Brooke Jude spoke to The Scientist magazine about her collaboration with microbiologist Anne Madden, who is founder and chief scientific officer of The Microbe Institute. Their collaboration, Find Purple, Frog-Saving Microbes, is a participatory science (citizen science) and community bioart project to conserve amphibians.
Brooke Jude Discusses Her Collaboration with Microbiologist Anne Madden to Save Amphibians
Post Date: 12-17-2024
Peter L’Official’s Essay “Black Builders” Published in Places Journal
Peter L’Official, associate professor of literature and director of the American and Indigenous Studies Program, explores the relationship between both writing and architecture, and race and design, in an essay for Places Journal. In examining the works of visionary Black architect and urban planner W. Joseph Black (1961–1977), novelist Colson Whitehead, and other scholars and writers, L’Official asks: “What do we learn about visions of cities when we consider writing and architecture as mutually defining?”Peter L’Official’s Essay “Black Builders” Published in Places Journal
L’Official’s “Black Builders” is the first essay in An Unfinished Atlas, a series funded by the Mellon Foundation and published by Places Journal that brings together scholars, cultural critics, essayists, and novelists of color to enrich the cultural record of place-based narratives across what is now called North America.
Post Date: 11-05-2024
Professor Susan Fox Rogers Leads Community Birding Walks on Cruger Island Road as Profiled in the Daily Catch
This spring, Susan Fox Rogers, visiting associate professor of writing, is leading Monday morning birding walks from 7 to 9 am down Cruger Island Road on Bard College’s campus. The walks, which will continue through May 27, draw an intergenerational audience and are part of a greater environmental education initiative at the Red Hook Public Library, where Rogers is the inaugural Ascienzo Naturalist in Residence.Professor Susan Fox Rogers Leads Community Birding Walks on Cruger Island Road as Profiled in the Daily Catch
Post Date: 04-16-2024
More EUS News
-
Bard College Receives $69,300 Grant from New York State Department of Conservation Hudson River Estuary Program
Bard College Receives $69,300 Grant from New York State Department of Conservation Hudson River Estuary Program
Bard College has received a $69,300 grant from the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation’s (NYS DEC) Hudson River Estuary Program. Bard’s grant is part of $1.8 million in total awards recently announced by Governor Hochul for 26 projects to help communities along the Hudson River Estuary improve water quality, enhance environmental education, and advance stewardship of natural resources. Funding will support Bard’s project to develop a “River Harmful Algal Blooms Watershed Characterization and Communication Toolkit,” which includes a Watershed Characterization report and communication materials focused on harmful algal blooms (HABs) in the Walkill River, an emerging water quality issue that can impact public health.
The Bard College Community Sciences Lab will partner with the Wallkill River Watershed Alliance, Hudson River Watershed Alliance, and Riverkeeper to develop a public-facing HABs Watershed Characterization report for the Wallkill River, a Wallkill River HABs Communications Toolkit to help coordinate effective public communications about future HABs, and a broader Water Issue Communications Framework for watershed groups or municipalities across the region to guide communications planning for HABs or other emergent and emergency conditions that affect public health.
“This funding is an important investment in community-directed stewardship of Hudson River waterways, and I applaud the DEC for recognizing this,” says Bard Associate Professor of Biology and Environmental and Urban Studies M. Elias Dueker, who is also codirector of the Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities, and head of the Community Sciences Lab. “With the increased pace of climate change, current policies regarding nutrient loading, stormwater management, and wastewater treatment simply are not keeping up with the increasing likelihood of algal blooms in our waterways as temperatures rise and precipitation regimes shift. Community scientists with a true sense of connection to these resources are a vital bridge between on-the-ground, real-time realities and the capacity for regulatory agencies to keep communities local to vulnerable waterways like the Wallkill safe. Community science is key to true climate adaptation and resilience, and I am thrilled to be part of this collaboration.”
Executive Director of Hudson River Watershed Alliance Emily Vail said: “The Hudson River Watershed Alliance is excited to be collaborating with scientists, local and regional organizations, and community members on this challenging and important issue. Harmful algal blooms can put people and pets at risk, and are an emerging threat in lakes and rivers. We’re looking forward to better understanding the latest science and communication strategies to keep people informed.”
Science Director of Riverkeeper Shannon Roback said: “Harmful algal blooms can pose health problems for both humans and animals who are exposed. As climate change progresses, we expect this risk to increase as blooms become more common. Effective public communication will be essential in reducing the harms. We are very excited that the NYS DEC Hudson River Estuary Program has funded our proposal to develop strategies to improve public outreach, communication and education around HABs, which we expect to have significant impacts to public health.”
“New York State is investing in projects that will improve resiliency and protect our natural resources both in the Hudson River Valley and across the state,” Governor Hochul said. “These 26 local grants will provide dozens of communities support to improve recreation, expand river access and education, and preserve and protect this iconic river for future generations of New Yorkers.”
Now in its 21st year, the Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) Hudson River Estuary Grants Program implements priorities outlined in the Hudson River Estuary Action Agenda 2021-2025. To date, DEC’s Hudson River Estuary Program awarded 643 grants totaling more than $28 million. Funding for DEC’s Estuary Grants program is provided by New York State’s Environmental Protection Fund (EPF), a critical resource for environmental programs such as land acquisition, farmland protection, invasive species prevention and eradication, recreation access, water quality improvement, and environmental justice projects. Governor Hochul’s proposed 2024-25 Executive Budget maintains EPF funding at $400 million, the highest level of funding in the program’s history.
Post Date: 03-05-2024
-
Bard College Institute for Writing and Thinking Hosts Conference on “Climate Change in the Classroom: Embracing New Paradigms” on April 26
Bard College Institute for Writing and Thinking Hosts Conference on “Climate Change in the Classroom: Embracing New Paradigms” on April 26
Bard College’s Institute for Writing and Thinking (IWT) will host its annual April Conference and welcomes educators of all disciplines on Friday, April 26 from 9:30 am to 4:30 pm. This year’s IWT conference will focus on “Climate Change in the Classroom: Embracing New Paradigms.” The conference will be hybrid, and participants can join online or in person at Bard’s Annandale-on-Hudson, New York, campus. Participants can learn more about the conference and register here.
The rate and severity of extreme climate events can bring on a feeling of numbness and resignation rather than catalyzing responsive resilience in the classroom. How can we refocus the conversation from crisis to education and adaptation? The 2024 IWT April Conference will conduct a deep dive into layered and often contradictory pedagogies about the natural world. This day of shared writing and reflection invites participants to join together in small, interactive workshop groups in order to explore a range of written, audio, visual, and hybrid texts—on topics from manifest destiny to global climate strikes—that are creating a new ecology of education.
The day will feature a plenary conversation by two Bard colleagues on the topic of climate change in the classroom from the perspectives of the humanities and STEM, respectively. Visiting Writer in Residence Jenny Offill is the author of three novels, Last Things, Dept. of Speculation, and most recently, Weather, which was shortlisted for the Women’s Prize for Fiction. Eli Dueker is associate professor of biology and environmental and urban studies at Bard, codirector of the Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities, and head of the Community Sciences Lab.
Tuition fees are from $450 to $575, with Early Bird (before March 26) and Group discounts. Scholarships are available by application here. The IWT conference is Continuing Teacher and Leader Education 5.5 credit hours. Register here.
Post Date: 02-20-2024
-
Bard College Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities Receives $44,892 EPA Grant to Improve Air Quality and Public Health Across Underserved Neighborhoods in New York State
Bard College Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities Receives $44,892 EPA Grant to Improve Air Quality and Public Health Across Underserved Neighborhoods in New York State
The Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities (CESH) at Bard College has received a $44,892 sub-award through the Research Foundation for SUNY Albany as part of a federal grant with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The grant will support a project with the overarching goal of improving air quality and public health across underserved neighborhoods in New York State by establishing a community driven network platform to enhance understanding of sustainable outdoor and indoor air quality. The Principal Investigator for this grant is Dr. Aynul Bari at SUNY Albany.
Through the Community Sciences Lab within CESH, Bard will provide technical and analytical support for the project over two years for study sites in the Hudson Valley, including sites in Kingston, Red Hook, Annandale-on-Hudson, Newburgh, and Poughkeepsie. Specifically, CESH will provide and install weather stations, with air quality and meteorology sensors, at Newburgh and Poughkeepsie sites; and support Dr. Bari’s group in monitoring indoor and outdoor air quality in 40 homes in the Hudson Valley over the next three years—testing for a broad range of air pollutants, including black carbon, volatile organic compounds, ultrafine particles, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and ozone. Bard student involvement will include supporting monitoring efforts (indoor and out) and using the air quality data to assess air quality challenges in the Hudson Valley in classes.
“We are incredibly thankful to Dr. Aynul Bari and the Research Foundation for SUNY Albany for including us in this EPA grant,” said M. Elias Dueker, associate professor of Environmental and Urban Studies at Bard. “We look forward to using these funds to expand our indoor and outdoor air quality work with groups like the Kingston Air Quality Initiative and the Hudson Valley Air Quality Coalition. The right to breathe clean air inside and outside our homes is not something we can take for granted as we wrestle with important climate-based challenges, including increased wildfire smoke plumes from other parts of the country, flood-induced molding of our aging housing stock, and increased wood burning in our valley communities.”
The Community Sciences Lab (CSL) was created to support the work conducted by CESH. Built on the success of the Bard Water Lab and its partnership with the Saw Kill Watershed Community (SKWC), CSL expands CESH’s reach by allowing us to refocus our work on projects that address the interconnectedness of land, air, water, and communities. CSL projects include: Saw Kill Monitoring Program, Roe Jan Monitoring Program, Kingston Air Quality Initiative, Bard Campus Station, Hudsonia Eel Project, and Amphibian Migration.
Post Date: 12-21-2023
-
Kingston Air Quality Initiative at Bard College Reports After Three Years of Monitoring
Kingston Air Quality Initiative at Bard College Reports After Three Years of Monitoring
The Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities at Bard College is pleased to announce the findings of the Kingston Air Quality Initiative (KAQI) after three consecutive years of research and data collection.
KAQI began in January 2020 as a partnership between Bard’s Community Sciences Lab and the City of Kingston Conservation Advisory Council’s Air Quality Subcommittee. Since then, Kingston residents and Bard College students, staff, and faculty have facilitated both indoor and outdoor air quality monitoring projects throughout Ulster County. Standing as the first air quality study of its kind in Kingston, KAQI’s monitoring efforts focus on a regional assessment of air pollution as measured from the roof of the Andy Murphy Neighborhood Center on Broadway in Kingston.
KAQI’s main monitoring efforts focus on a regional assessment of air pollution from fine particulate matter (PM2.5), made up of microscopic particles that are the products of burning fuel, and is released into the air through exhausts from oil burners, gas burners, automobiles, cooking, grilling, and both indoor and outdoor wood burning. PM 2.5 particles are so tiny, they stay suspended in the air for long periods of time, allowing them to travel long distances before depositing. When these particles are inhaled, they can enter the bloodstream through the lungs, creating or exacerbating health issues. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that “small particulate pollution has health impacts even at very low concentrations – indeed no threshold has been identified below which no damage to health is observed.”
After 3 years of monitoring in Kingston, air quality trends associated with daily activities are observable. The findings show that air pollution in the city is variable and appears to have a seasonal context—higher levels of pollution are shown during colder months (associated with fuel burning), and lower levels are generally seen in spring and summer. The difference between levels seen during 2020—when COVID shut down many activities and resulted in a decrease in vehicles on the road—and pollution levels detected in years since is also significant.
Two important measures of PM2.5 air quality are the annual mean standard and the 24-hour average standard. Kingston’s PM2.5 air quality met the annual standards of both the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the WHO, although it came close to exceeding the latter. For the 24-hour standard, air quality met the EPA’s but exceeded the WHO’s.
As of January, 2023, a revision was proposed to change the EPA's primary public health-based annual standard from its current level of 12.0 micrograms per meter squared to the range of 9.0-10.0 micrograms per meter squared. This revision would lean closer toward, but not come close to meeting, the WHO's PM 2.5 annual standard of 5 micrograms per meter squared. Based on the EPA annual mean calculations, these values come close to exceeding the WHO annual standard.
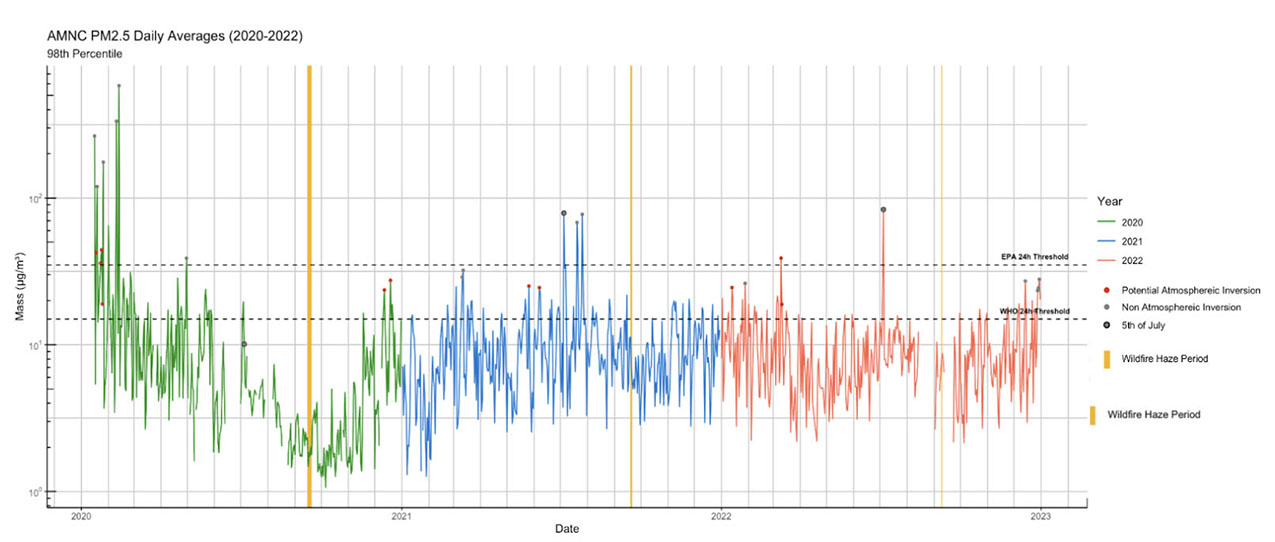
One factor associated with instances of air quality breaching the WHO’s 24-hour threshold is the development of atmospheric inversions, which occur when the temperature of the atmosphere increases instead of decreases with altitude and surface level air parcels are unable to rise up, trapping any present air pollution at ground level. Being in the Hudson Valley, Kingston is more susceptible to inversion events as the air is blocked from all directions. It's possible that, if Kingston residents were aware of when these events are occurring, we could start making different decisions about woodburning and car use during these times to make our air cleaner for all. Another potential factor may be pollutants from smoke carried from wildfires on the West Coast.
More detail about KAQI’s findings can be found at the Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities website: https://cesh.bard.edu/kingston-air-quality-initiative-kaqi/
“While our annual averages meet EPA standards, as many residents of Kingston and the surrounding areas know, air quality at ground level can vary widely from neighborhood to neighborhood,” said Lorraine Farina, co-founder of KAQI and the Hudson Valley Air Quality Coalition, and former Kingston CAC air quality sub-committee chair. “The average adult takes in 1000 breaths per hour, and exposures to dangerous fine particulate matter very much depend on whether wood is being burned nearby, as burning wood is dirtier and more polluting than burning oil, gas, or coal. There is no safe level of exposure to PM 2.5, so the expanding neighborhood-level monitoring efforts of the Bard Community Science Lab will help residents understand the actual air quality right where they are breathing, so we can all make choices that benefit both our health and that of the planet.”
“I want to thank Bard and the Community Sciences Lab for allowing Kingston to participate in this initiative,” said Steve Noble, the mayor of Kingston. “I am pleased to see that our air quality is superior to many of the places around us, but it’s a profound reminder that our daily activities do impact our health, and the health of our environment. We appreciate Bard’s investment in monitoring Kingston’s air, as it has been an invaluable learning tool. Together with Kingston’s Conservation Advisory Council, we will continue to monitor local air quality alerts, and will continue to work together with leaders in our region on policy and initiatives for cleaner air.”
Dr. Eli Dueker, co-director of the Bard Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities, added, “Clean air is something we often take for granted in the Hudson Valley. Our findings show that meeting annual EPA standards (particularly current standards) is one thing, but on a day-to-day basis, our air quality is sometimes degraded and can be unhealthy. After all, we are not breathing on an average yearly basis—we are breathing on a second-by-second basis. We can make decisions as a community to keep our own air clean – for example, we could reduce or even stop our wood-burning in city limits (particularly on days with atmospheric inversions), reduce our car use, and make our homes more energy efficient.”
The Center for Environmental Sciences and Humanities at Bard College, in collaboration with KAQI, has been working on a handful of air quality related projects centralized around community needs and concerns. These include:- Developing a publicly-accessible atmospheric inversion monitoring system for the Kingston area.
- Neighborhood-level air quality monitoring, through the fast-developing Hudson Valley Library Air Quality Network. Using outdoor real-time air quality monitoring devices stationed at public libraries, air quality data is free and accessible online. We are always looking for new locations throughout the Hudson Valley to add to the network and provide more localized data for residents. If any libraries are interested, please reach out to [email protected].
- In partnership with SUNY-Albany, conducting indoor and outdoor air quality monitoring in homes with woodsmoke, mold and structurally-related air quality challenges.
For more information or ways to get involved, please visit https://kingston-ny.gov/airquality or https://cesh.bard.edu/kingston-air-quality-initiative-kaqi/.
Post Date: 06-06-2023
-
Bard Student Research on Housing Justice Cited in Times Union Article “Evicted in Kingston: Voices from a Crisis”
Bard Student Research on Housing Justice Cited in Times Union Article “Evicted in Kingston: Voices from a Crisis”
According to a recent Times Union article, the city of Kingston, New York, doesn’t keep track of corporate housing ownership. “But Kwame Holmes, a professor at Bard, and his class did a deep dive on a chunk of Midtown Kingston in 2020, which led to some revealing findings,” the article cites. “Of 481 Midtown properties, non-locals owned 275 . . . Limited liability corporations owned 87 properties, 10 of which shared names with corporate landlords operating in states across the country.”
In 2020, Kwame Holmes, scholar in residence in the Human Rights Program at Bard, taught a class that examined how housing inequity manifests in Kingston and other areas of Ulster County. Holmes and 13 of his students geocoded and collected information on hundreds of properties in Kingston’s Midtown section to study the data on property ownership and its impacts on the city’s residents. “These dynamics illustrate the extent to which land in Kingston is a site of profit extraction, and very little of that capital directly benefits local residents,” states the Bard report, which produced findings that were shared with community leaders and stakeholders. The class, Housing Justice Lab, was a collaboration of Bard’s Environmental and Urban Studies and Human Rights programs and part of the Bard Center for Civic Engagement Engaged Liberal Arts and Sciences Program.
Further Reading
Bard College Human Rights Professor and Students Study Urban Displacement and Gentrification with Kingston Housing Lab
Post Date: 05-16-2023
-
Myra Young Armstead Spoke with the Times Union about the Life and Legacy of James F. Brown, “One of the Country’s First Black Master Gardeners”
Myra Young Armstead Spoke with the Times Union about the Life and Legacy of James F. Brown, “One of the Country’s First Black Master Gardeners”
While slave narratives—“first-person retellings of the enslaved experience”—were persuasive to white abolitionists and widely distributed, quieter but no less important details about the early years of emancipation can be found in the diaries of one of the country’s first Black Master Gardeners, James F. Brown. Myra Young Armstead, vice president for academic inclusive excellence and Lyford Paterson Edwards and Helen Gray Edwards Professor of Historical Studies, spoke with the Times Union about Brown’s life and legacy. “In the period before the Civil War, freedom in the most obvious sense for a runaway meant emancipation,” Armstead said. “It also meant freedom from wage slavery, and freedom to operate in the civic sphere. We can explore the many meanings of freedom in the antebellum period through James’s diary.”
Post Date: 02-14-2023
EUS Events
There are no events to display.